
Threat Intelligence Strategies for MSSPs
As cyber threats continue to evolve in both complexity and frequency, the role of Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) is becoming increasingly critical. Many companies now prefer to outsource their cybersecurity to MSSPs in order to focus on their core business. To stay ahead of these imminent threats, MSSPs have been incorporating cyber threat intelligence (CTI) into various aspects of their cybersecurity initiatives.
Threat intelligence provides you with the necessary insights to more effectively detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. This helps you achieve maximum protection for your clients. By leveraging CTI, not only are you able to counter ongoing cyber attacks, but you can also preempt potential attacks.
That said, the continuously evolving nature of cyber threats is nevertheless posing significant challenges to traditional threat intelligence strategies. With threats becoming more sophisticated, frequent, and diverse, the static security strategies of old are proving to be insufficient. Adversaries are constantly devising new attack methods, including Zero-day attacks and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), which traditional threat intelligence methods struggle to anticipate and counter.
Furthermore, the increasing interconnectedness of digital infrastructure, use of cloud computing services, and adoption of remote work has amplified the attack surface, has been making it harder to monitor and secure every potential vulnerability.
To keep pace with the evolving nature of cyber threats, we must adapt new CTI strategies. In this post, we’re taking a deep dive into new CTI strategies and explain how each of these strategies help you deal with the evolving cyberthreat landscape.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Let’s start with what is undoubtedly the hottest new trend that’s advancing rapidly not only into CTI and cybersecurity in general, but also into other aspects of our lives: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
What came before
Traditional threat intelligence implementations largely relied on manual or semi-automated processes. These methods were heavily dependent on the expertise of the security analysts and the quality of the threat intelligence data on hand.
While somewhat effective, traditional CTI had significant limitations. For one, it was time-consuming and resource-intensive. Plus, it was hard to scale, especially with the never-ending cybersecurity skills gap. Searching for security analysts skilled in CTI these days is like looking for a needle in a haystack.
Moreover, these traditional strategies struggled with accurately predicting and combating unknown threats. They were not equipped with the tools necessary to detect subtle patterns or anomalies indicative of a potential cyber attack. This often resulted in delayed threat detection, leading to significant damage before defensive and remedial measures could be brought into play.
Before AI and ML integration became a thing, CTI strategies were essentially reactive, often only identifying and addressing threats after they had already infiltrated the network. AI and ML technologies bring remarkable improvements to the speed and accuracy of threat intelligence.
How MSSPs are leveraging AI/ML to enhance CTI
The ability of AI/ML to analyze vast amounts of data at a speed that far surpasses human capabilities paves the way for real-time threat detection and rapid response. AI and ML can sift through billions of data points, identify patterns, and learn from historical data to accurately detect and even predict potential threats faster than humans can.
Moreover, these technologies excel in detecting zero-day vulnerabilities and advanced persistent threats (APTs) that often evade traditional security measures. By continuously learning from each interaction, AI and ML can adapt and evolve, ensuring that the threat detection strategies employed are always a step ahead of emerging threats.
This proactive approach to cybersecurity greatly reduces the window of exposure, ensuring threats are neutralized before they can cause significant harm. In turn, AI/ML integrations free up bandwidth for security analysts by automating routine tasks, which then allows the analysts to focus on more pressing cybersecurity endeavors.
MSSPs are increasingly leveraging AI-driven tools to bolster their threat intelligence and analysis capabilities. AI/ML integrations are enabling MSSPs to identify potential threats that might otherwise go unnoticed in a huge data pool.
With AI, you can speed up the routine but time-consuming task of sifting through CTI data and data logs, detecting anomalies, and identifying patterns indicative of a cyberattack. AI-driven tools are transforming the threat intelligence strategies of MSSPs, making them faster, more efficient, and proactive.
Increased use in Proactive Threat Hunting
Proactive threat hunting is another field witnessing an upsurge within the cybersecurity landscape. Unlike traditional reactive measures, proactive threat hunting focuses on proactively searching, identifying, and isolating threats before they escalate into a business-impacting cyber incident. This hands-on approach to security, now often enabled by advanced AI and ML technologies, is transforming the way MSSPs operate.
What came before
The use of CTI in threat hunting isn’t exactly new. Cybersecurity practitioners have long been using threat intelligence data to help them uncover threats that have infiltrated their networks. They’ve been doing this even before the term “threat hunting” became a buzzword. It is however worth noting that this type of threat hunting was more reactive in nature. They were often performed in response to an ongoing or recently-detected cyber incident.
CTI feeds are a common source of updates regarding known threats as well as Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) such as IP addresses, domains, hashes, and URLs associated with those threats. However, threat hunters haven’t been as dependent on CTI data as they are now.
How MSSPs are using CTI in threat hunting
One of the major reasons for the increased dependence of threat hunting on CTI is the rise of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). These threats are typically orchestrated by nation states, who have almost unlimited resources and advanced capabilities to launch sophisticated attacks. APTs often exploit zero-day vulnerabilities and are able to breach seemingly robust cyber defenses as well as persist in the target’s environment undetected for long periods of time.
The inability to detect APTs is currently the biggest challenge faced by most Security Operations Centers (SOCs). In this context, CTI has become a crucial tool in informing threat hunters about the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) that APT groups are likely to employ as well as the IoCs associated with them.
By leveraging CTI, threat hunters can better hone in on the most relevant attack vectors and uncover stealthy adversaries, including APTs, before they carry out business-impacting security incidents. One of the main goals of this type of threat hunting is to uncover a threat early in its cyber kill chain. Hence the term ‘proactive threat hunting’.
Incidentally, both proactive threat hunting and threat intelligence were identified in the Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 among the key cost mitigators of data breaches. ‘Cost mitigators’, in the context of this report, refer to those measures or strategies that help reduce the financial impact of a data breach.
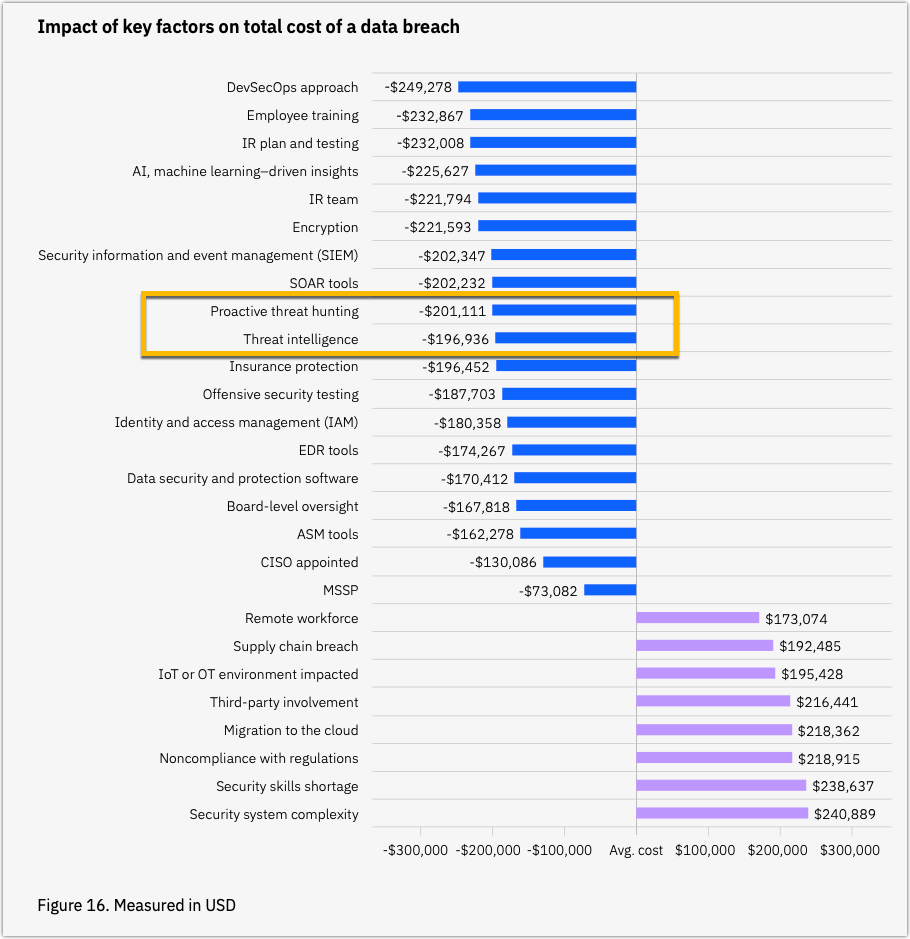
You can leverage CTI to streamline proactive threat hunting efforts in their clients’ IT environments. By integrating CTI into your security strategies, you can be better equipped at nipping adversaries in the bud and reduce client risk of suffering a data breach.
Zero Trust Architecture and Threat Intelligence
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) as we know it was introduced some time in the mid-2010s and started gaining traction in the later part of that decade. In other words, it’s relatively new. But with the announcement of the US government’s new National Cybersecurity Strategy earlier this year, we expect even greater adoption of ZTA.
The new National Cybersecurity Strategy is putting more emphasis on ZTA. This increased emphasis signifies an acknowledgment of the fact that perimeter defense tactics are inadequate in today’s threat environment, and that trust must be continually earned and validated, not just assumed.
Zero Trust Architecture fundamentally shifts network design from a static, perimeter-based model to a dynamic, identity-centric strategy that treats all users and entities as potential threats until evaluated, authenticated, and authorized.
In the ZTA, every access and connection request is fully vetted before it is granted while ensuring continuous verification during the entire session. CTI can play an instrumental role in this process. CTI can provide actionable information about potential threats and vulnerabilities, which can then be utilized by ZTA in the decision-making process for granting access.
Threat intelligence can, for example, provide insights into whether a request is part of a larger attack pattern or linked to a known threat, thus enabling more informed and accurate decisions in allowing or denying access.
In fact, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in its Special Publication 800-207 states that threat intelligence can play a vital role in the planning and design of Zero Trust Architecture. NIST suggests that organizations incorporate threat intelligence into their ZTA to ensure a more robust defense against cyber threats.
MSSPs are currently harnessing the power of ZTA in their strategies by implementing rigorous and dynamic access controls. These controls scrutinize and verify every access and connection request based on real-time threat intelligence. Whenever an access request or connection attempt is found to be related to a known threat, it is automatically blocked.
The pivot towards Zero Trust Architecture combined with threat intelligence allows you to stay ahead of potential threats and maintain an effective defense for your clients.
Applied Threat Intelligence (ATI) – A Game Changer for MSSPs
The task of managing Cyber Threat Intelligence effectively represents a significant challenge for many MSSPs. This is due in large part to the sheer volume of work associated with CTI, especially when you have to combine CTI with threat detection and response.
The work starts with collecting an immense amount of raw data from multiple sources, including open-source intelligence (OSINT), social media intelligence, human intelligence, and others. This raw data then needs to be analyzed to filter out the noise and identify the actual threats. This involves correlation, normalization, and aggregation of data, which in itself is a time-consuming and error-prone process.
Once potential threats have been identified, they must be thoroughly investigated. This includes understanding the threat actor’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and assessing the potential impact and risk to the organization.
Moreover, the work doesn’t end there. After a threat is validated, you must develop and implement appropriate responses. This may involve crafting and implementing new security rules and protocols on their threat detection and protection tools. And then once an attack finally takes place, they’d have to carry out incident response.
Indeed, the workload associated with CTI and threat detection and response can inundate even the most dedicated MSSPs. It’s a constant, relentless cycle of data collection, analysis, validation, response, and monitoring. This is where Applied Threat Intelligence (ATI) can make a significant difference.
Applied Threat Intelligence (ATI) is a proactive and aggressive approach you can adopt to enhance your cyber defense. This approach involves the real-time application of threat intelligence to detect and prevent potential cyber attacks. It can stop an attack in its tracks early in its cyber kill chain.
Intrusion uses one of the world’s largest known repositories of IP and domain reputation knowledge, which is continuously updated with newly discovered threat information. This vast database, combined with AI analytics, allows Shield to effectively differentiate between harmful and benign activities, reducing false positives and ensuring a more secure environment.
This high level of breach detection and prevention correlates with the principles of Zero Trust Architecture. Every access request is analyzed and only granted if it passes the stringent checks, thus aligning with the “Never Trust, Always Verify” principle of ZTA. This also means that anything unknown is blocked by default.
By partnering with Intrusion, you can offer your clients an advanced, resilient cyber defense. By incorporating this sophisticated ATI tool into your strategy, you can also play a pivotal role in the National Cybersecurity Strategy. You can help organizations establish a robust Zero Trust Architecture, fortified by real-time threat intelligence, a key requirement for effective cybersecurity in today’s complex digital landscape.
Want to know more about Intrusion Shield and ATI? Chat with a cybersecurity expert now.


